Managing a verdant, flourishing garden requires knowledge of the unwelcome guests that may invade it: weeds. An understanding of common types of weeds, their characteristics, and the ways to control them is crucial for garden enthusiasts. This post will delve into some prevalent types of weeds and offer insights on how to identify and remove them effectively. Whether a seasoned gardener or a beginner, this guide will equip you with the necessary know-how to keep your garden thriving and weed-free.
Contents
Canada Thistle (Cirsium arvense)
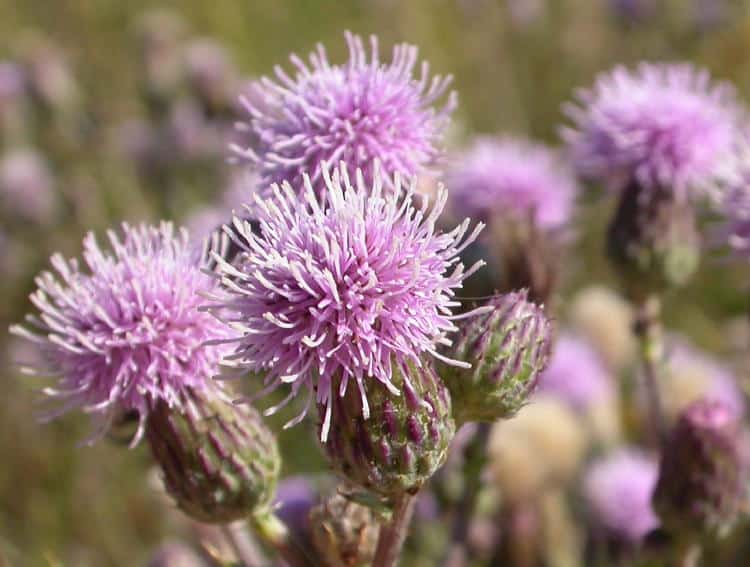

Canada thistle is a persistent and widespread weed, easily recognizable by its prickly leaves and purple or white flowers. Originating from Europe, it poses a significant problem for North American gardeners due to its extensive root system that can grow deep and spread wide, making it hard to control.
Effective removal of Canada thistle requires consistent effort. Cutting the thistle back repeatedly can eventually starve the plant, as it relies on photosynthesis to sustain its vast root system. Alternatively, non-toxic herbicides based on concentrated vinegar can also be employed to control its growth. It’s important to note that the process requires patience as it may take more than a single season to completely eradicate this stubborn weed.
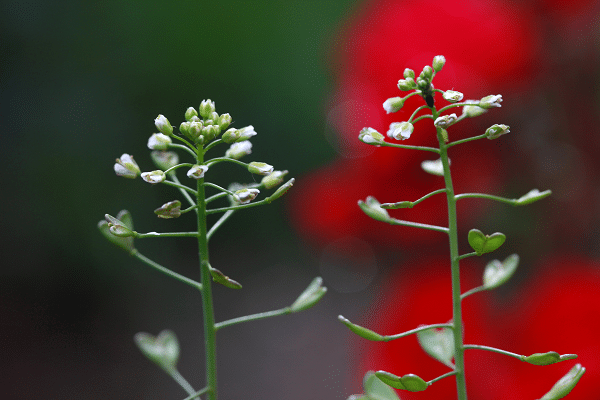
Shepherd’s Purse (Capsella bursa-pastoris)
Shepherd’s Purse is a common annual and winter annual weed, found almost everywhere around the globe. It derives its name from the distinct, heart-shaped seed pods that resemble an old-fashioned leather pouch or purse. Characterized by its rosette of deeply lobed leaves at the base and small white flowers, this weed can become a nuisance in gardens and lawns due to its prolific seed production.
Management of Shepherd’s Purse begins with the timely removal of young plants before they reach the flowering stage and start producing seeds. A hand weeder can be used to uproot the plant, ensuring that the entire root is removed to prevent regrowth. For a more extensive infestation, a broad-spectrum or selective post-emergence herbicide can be considered. In either case, maintaining a well-nourished and dense lawn or garden is an effective preventative measure, as it leaves little room for this weed to establish. Consistent monitoring and early intervention are the best strategies to keep Shepherd’s Purse under control.
Crabgrass (Digitaria)
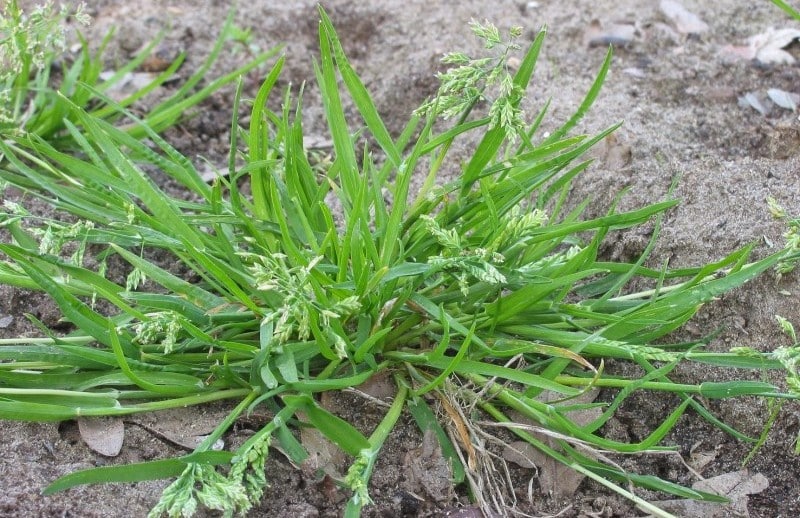

A warm-season annual weed, crabgrass thrives in full sunlight and high temperatures. It is identified by its finger-like blades that spread out from a central point, resembling a crab—hence the name. Crabgrass is opportunistic, capitalizing on thin, bare spots in the lawn where it quickly germinates and establishes itself.
Removal strategies for crabgrass focus on maintaining a healthy, dense lawn to crowd out potential invaders. Regular watering and fertilizing help maintain the vitality of the lawn, making it less hospitable for crabgrass. Pre-emergent herbicides can also be applied in the early spring to prevent crabgrass seeds from sprouting. Remember, timing is critical since these herbicides lose their effectiveness once the weed has germinated.
Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale)
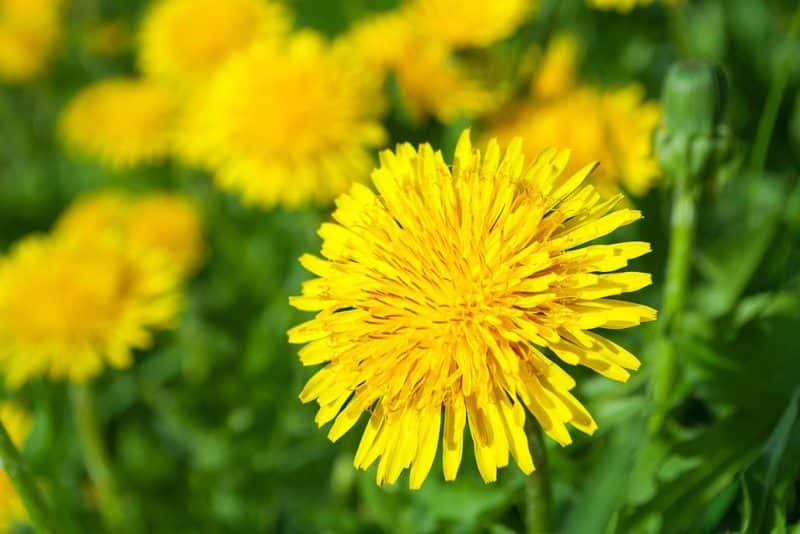

Dandelions are ubiquitous weeds with bright yellow flowers and distinct, serrated leaves. Although they can sometimes be used for culinary or medicinal purposes, dandelions are typically unwelcome in lawns due to their quick spreading and resilience.
For dandelion removal, a combination of manual extraction and preventative maintenance is recommended. Using a weeding tool, dandelions should be removed from the root to prevent regrowth. Post removal, attention should be given to lawn health. A lush, well-nourished lawn leaves little room for dandelions to take hold. Organic or chemical-based herbicides can also be used if the infestation is extensive, but these should be applied with caution to avoid damaging desirable plants.
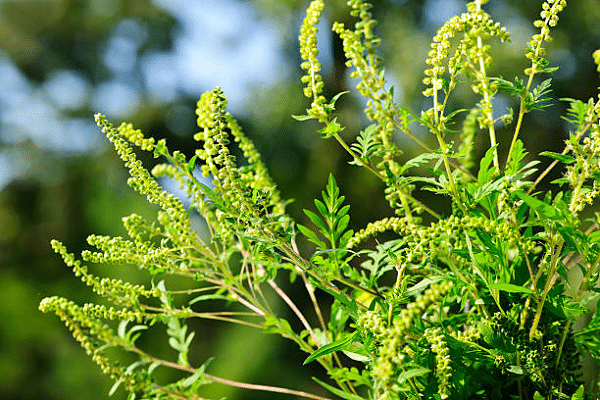
Ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia)
Ragweed is a highly allergenic plant and a common bane for those who suffer from hay fever. Its light, feathery seeds are easily carried by the wind, which explains why it can spread so rapidly and broadly. Identified by its deeply lobed leaves and small, greenish-yellow flowers, this weed thrives in disturbed soils and can reach up to four feet in height.
Effective ragweed management combines vigilant removal and healthy lawn practices. It’s vital to pull out these weeds before they get the chance to release their seeds, ideally when the soil is moist to ensure complete removal of the root. Beyond this, maintaining a thick, nutrient-rich lawn can hinder ragweed growth, as this weed prefers sparse, nutrient-poor soil. Use of selective herbicides may also be considered, but they should be applied judiciously to minimize impact on non-target plants and organisms.
Yellow Sweet Clover (Melilotus officinalis)
Yellow Sweet Clover is a biennial weed identifiable by its trifoliate leaves and small, sweet-smelling, yellow flowers. This weed, originally from Eurasia, is often used as a green manure or forage crop but can become invasive in lawns and gardens.
Controlling Yellow Sweet Clover requires timely and thorough removal. As a biennial, this weed lives for two years, producing foliage in the first year and flowering in the second. Removing the plant before it flowers and sets seed is essential to prevent spread. When pulling the weed, ensure to remove the entire root to avoid regrowth. If the infestation is widespread, a selective broadleaf herbicide can be a practical option, as long as its application aligns with the product’s instructions and safety precautions.
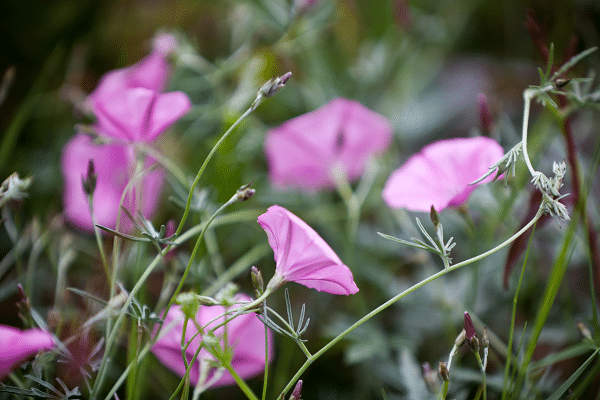
Bindweed (Convolvulus arvensis)
Bindweed is an invasive perennial vine with arrowhead-shaped leaves and trumpet-like white or pink flowers. Often mistaken for Morning Glory, bindweed can become a major problem due to its aggressive growth and ability to reproduce both through seeds and its extensive root system.
For successful bindweed management, persistence is key. Regular, diligent removal of the vine from the surface can gradually weaken the plant and reduce its root reserves. If the infestation is extensive, the use of a systemic herbicide, which the plant absorbs and transports down to its roots, might be required. However, care must be taken to ensure that the herbicide doesn’t affect desirable plants. As with many of these tough-to-control weeds, it may take more than one season of diligent effort to gain control over a bindweed infestation.
Conclusion
Understanding the characteristics of common weeds and how to manage them effectively is a cornerstone of successful gardening. Through consistent effort, proper lawn care, and strategic use of manual and chemical methods, even the toughest weeds like Canada Thistle, Shepherd’s Purse, Crabgrass, Dandelion, Ragweed, Yellow Sweet Clover, and Bindweed can be controlled. Readers are invited to share their experiences and pose questions in the comment section below. Remember, in the world of gardening, knowledge is the greatest tool.