As the chill of winter sets in, gardeners and plant enthusiasts face a unique set of challenges. While the cold weather brings a respite from some pests and diseases, it also ushers in an array of plant diseases that thrive in the cooler, often wetter conditions. Understanding these diseases, their symptoms, and how they affect various plants is crucial for maintaining healthy gardens and indoor plants during the winter months. This article delves into the common types of winter plant diseases, the environmental factors that contribute to their spread, and practical tips for identification, prevention, and treatment.
Contents
- 1 Common Types of Winter Plant Diseases
- 2 Environmental Factors Contributing to Winter Diseases
- 3 Symptoms and Identification
- 4 Plants Most Vulnerable to Winter Diseases
- 5 Prevention Strategies
- 6 Treatment Options
- 7 Long-term Management and Care
- 8 The Role of Professional Help
- 9 Safeguarding Plants Against Winter Woes
Common Types of Winter Plant Diseases
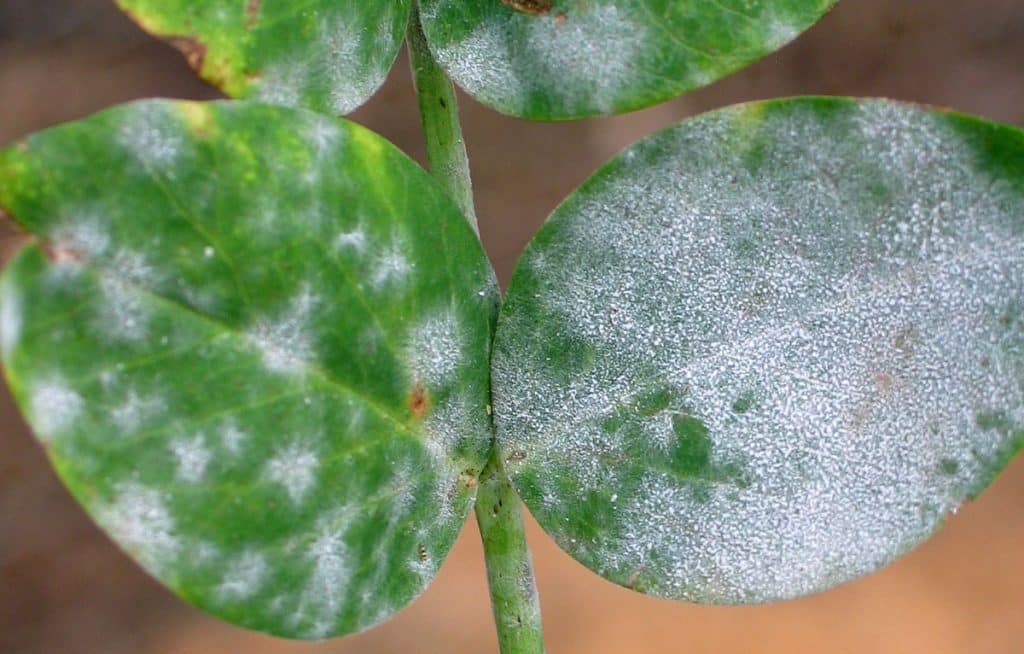
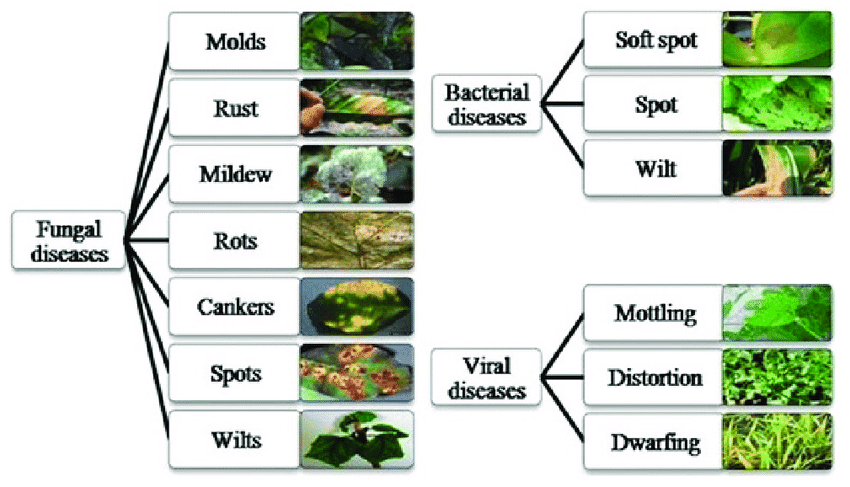
Winter brings a host of plant diseases, primarily caused by fungal, bacterial, and viral pathogens. Fungal diseases like powdery mildew and botrytis are prevalent due to the damp conditions, thriving in the lack of sunlight and poor air circulation. These fungi often manifest as white, powdery spots on leaves and stems, gradually weakening the plant. Bacterial diseases, such as bacterial blight, can rapidly spread in winter, especially in crowded plantings where moisture lingers on leaves and stems. These bacterial infections usually cause dark, water-soaked spots, often leading to leaf drop. Viral diseases, though less common, can also be problematic in winter, characterized by stunted growth and mottled leaves.
Environmental Factors Contributing to Winter Diseases
Several environmental factors during winter contribute significantly to the prevalence of plant diseases. Reduced sunlight during the shorter days of winter leads to weaker plant growth, making them more susceptible to infections. This lack of strong sunlight also prevents the quick drying of foliage, creating an ideal environment for fungal and bacterial growth. Prolonged wet conditions, typical in winter, coupled with high humidity, provide a perfect breeding ground for many pathogens. Additionally, fluctuating temperatures, common in late autumn and early winter, can stress plants, making them more vulnerable to diseases that they might otherwise resist during more stable conditions.
Symptoms and Identification
Recognizing the symptoms of winter plant diseases is key to timely and effective treatment. Common symptoms include discoloration of leaves and stems, wilting, and the appearance of spots or blotches on leaves. Fungal infections often present as powdery or downy growths on the plant’s surface, while bacterial infections result in wet, slimy areas on leaves and stems. Viral diseases typically cause distorted growth patterns, yellowing of leaves, and reduced vigor. To accurately identify these diseases, gardeners should look for patterns in symptom development, such as the progression of leaf spots or the spread of discoloration. Including images or diagrams can help readers visualize these symptoms for better identification in their own plants.
Plants Most Vulnerable to Winter Diseases
Certain plants are particularly susceptible to winter diseases, both in outdoor gardens and indoor settings. Outdoor plants like roses, rhododendrons, and fruit trees often fall prey to fungal diseases like rust and blight due to the moist conditions. Indoor plants, including orchids and African violets, are also at risk, especially when overwatered or lacking adequate airflow. These plants, along with others like tomatoes and cucumbers grown in greenhouses or indoor environments, require special attention during the colder months to prevent disease onset. Factors like plant genetics, previous disease history, and current health status play significant roles in their vulnerability to winter diseases.
Prevention Strategies
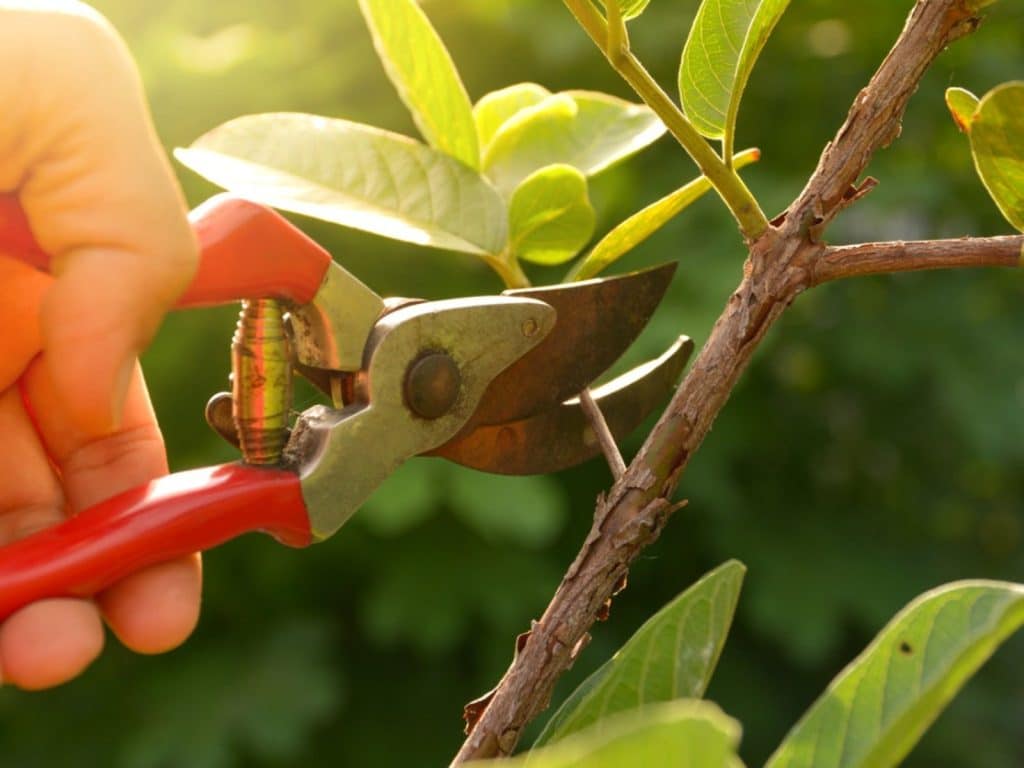
Preventing winter plant diseases starts with proactive and strategic care. Effective prevention methods include proper pruning to ensure good air circulation and reduce moisture retention on the plant surfaces. Spacing plants appropriately is crucial to avoid overcrowding, which can lead to a higher humidity environment conducive to disease spread. Gardeners should also consider planting disease-resistant varieties, which can significantly reduce the prevalence of certain diseases. Sanitation practices, such as removing fallen leaves and debris and avoiding overhead watering, can also help in minimizing the risk of disease. Regular inspection of plants for early signs of disease is key to preventing widespread infection.
Treatment Options
Once a plant disease is identified, timely and appropriate treatment is essential. For organic gardening enthusiasts, natural fungicides and bactericides, such as neem oil or baking soda solutions, can be effective in managing mild fungal and bacterial infections. These treatments are environmentally friendly and safe for use around children and pets. Chemical treatments, while more potent, should be used judiciously and according to manufacturer instructions to avoid harming the plant or the surrounding ecosystem. Timing is critical in treatment application, with early intervention often being the most effective. Gardeners should also consider the lifecycle of the disease-causing organism to determine the best time for treatment application, ensuring maximum efficacy.
Long-term Management and Care
Effective long-term management of winter plant diseases involves continuous monitoring and care adjustments. Regularly inspecting plants for early signs of disease, even after treatment, is crucial to prevent recurrence. This involves looking for subtle changes in leaf color, texture, or overall plant vigor. Gardeners should also adjust their care routines to suit the changing needs of plants during winter, such as modifying watering schedules and ensuring adequate light exposure. Adaptation to seasonal changes, like increasing humidity levels indoors during the heating season, can also play a significant role in maintaining plant health. Additionally, building up soil health with organic matter and ensuring proper nutrition can strengthen plants’ natural defense systems, making them less susceptible to diseases.
The Role of Professional Help
There are times when the expertise of a plant pathologist or a horticulturist is invaluable, especially for diagnosing and treating complex or persistent plant diseases. Professional help can offer accurate diagnosis, which is critical for effective treatment. Experts can also provide tailored treatment plans, considering the specific needs and conditions of your garden or indoor plants. Seeking professional advice is particularly recommended for widespread or recurring problems that have proven resistant to standard treatment methods. Gardeners can find local experts through extension services, gardening clubs, or professional organizations. These resources not only assist in disease management but also offer valuable knowledge and tips for overall plant care and maintenance.
Safeguarding Plants Against Winter Woes
By understanding the types of diseases, their symptoms, and the environmental factors that contribute to their spread, gardeners can effectively prevent and treat these issues. Regular monitoring, adopting preventive strategies, and seeking professional help when needed are essential steps. With these insights and actions, gardeners can ensure their plants not only survive but thrive during the winter, maintaining healthy and vibrant gardens and indoor plant collections.