Growing an organic vegetable garden is more than just a trendy hobby; it’s a step toward a healthier lifestyle and a more sustainable planet. Cultivating your food brings you closer to nature, provides you with fresh and nutritious produce, and reduces your carbon footprint. Moreover, tending to a garden has been found to offer numerous mental health benefits, including stress relief and improved mood. In this post, several key aspects of successful organic vegetable gardening will be explored, from natural pest control to picking the right vegetables for your climate and the use of organic soil and fertilizers.
Contents
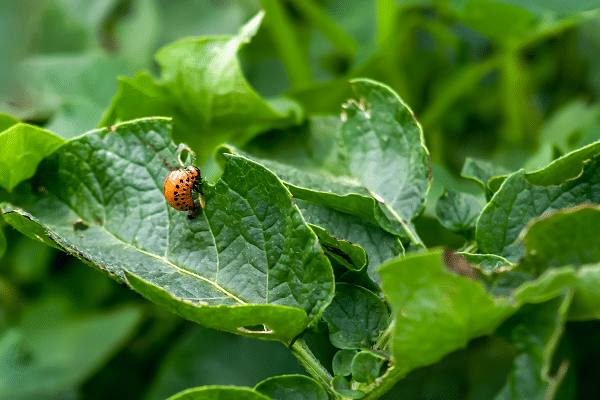
Keep Pests Away Naturally
Every gardener’s nightmare, pests can wreak havoc in even the most meticulously maintained vegetable garden. Instead of resorting to chemical pesticides, which are not only harmful to the environment but also to the plants and humans, it’s possible to use eco-friendly alternatives. Companion planting, for instance, is a method where certain plant species are grown together because they naturally repel pests. Marigolds, for example, are known to keep away a variety of insects and are, therefore, a great addition to any vegetable garden.
Beyond companion planting, homemade sprays can also offer a solution. Ingredients commonly found in kitchens, such as garlic, chili pepper, and vinegar, can be mixed into a spray that keeps pests at bay. It’s important to remember, however, that these sprays should be used sparingly and only when necessary to maintain the balance in the garden ecosystem.
Select The Right Vegetables For Your Climate
An organic garden’s success largely depends on the types of vegetables chosen and how well they adapt to the local climate. Each vegetable species has specific requirements for sunlight, temperature, and rainfall, so understanding these needs can increase your garden’s productivity. For instance, tomatoes and peppers thrive in warmer climates, while broccoli and lettuce do well in cooler ones.
Climate isn’t the only factor to consider when choosing vegetables. Soil type, space available, and the gardener’s personal preferences also play an important role. It might be tempting to grow exotic vegetables, but the best approach for beginners is to start with easy-to-grow vegetables that are known to do well in their region. Research, planning, and a bit of trial and error can help find the perfect mix of vegetables for your organic garden.
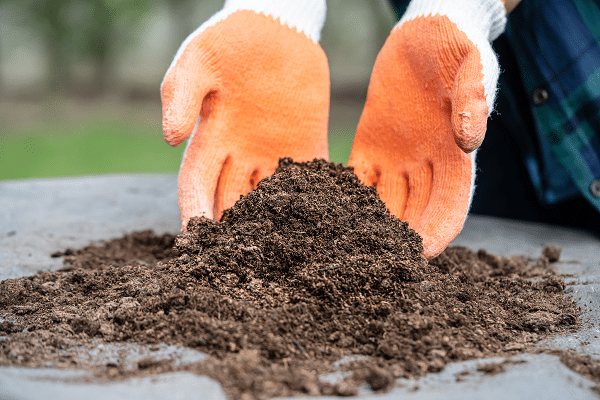
Use Organic Soil And Fertilizers
A successful organic garden starts from the ground up – with the soil. Organic soil, rich in nutrients and beneficial microorganisms, plays a crucial role in plant health and growth. Ensuring the soil is enriched with compost or well-rotted manure can enhance its fertility, structure, and water-holding capacity. One effective way of creating organic soil is through composting kitchen waste, garden clippings, and other organic material. This reduces waste, while providing nutrient-rich compost for the garden.
When it comes to fertilizing, chemical options are a no-go in organic gardening. Instead, homemade compost, worm castings, and organic fertilizers are the way to go. These provide the necessary nutrients for plants, improve soil structure, and encourage beneficial soil microbes, leading to healthier, stronger plants.
Crop Rotation And Polyculture
Crop rotation and polyculture are time-honored practices that can enhance the health and yield of an organic vegetable garden. Crop rotation involves changing the location of specific crops each year, reducing the chances of disease and pest infestation, and maintaining soil fertility. This practice is effective because different plants have varying nutritional needs and pest profiles. By changing their location, the soil’s nutrients are used more efficiently, and pests cannot become established.
Polyculture, on the other hand, refers to growing multiple crop species in the same space. This method increases biodiversity, can improve pollination, and reduces pest issues by not providing a large, single-species target. Polyculture also helps utilize garden space more efficiently by allowing crops with different growth habits to coexist, such as combining taller plants with ground-covering ones.
Watering And Irrigation Techniques
Water is life, especially for an organic vegetable garden. Efficient watering practices not only ensure the survival and health of your plants but also conserve a precious resource. Watering should be done early in the morning or late in the evening to reduce water loss through evaporation. It’s also vital to water at the plant’s base, keeping the foliage dry to prevent disease.
The ideal irrigation system for an organic garden should be efficient, sustainable, and easy to manage. Drip irrigation and soaker hoses are excellent choices as they deliver water directly to the plant’s root zone, reducing water wastage and keeping the foliage dry. Collecting rainwater is another good practice for organic gardening, providing a free, sustainable water source and helping manage stormwater runoff.
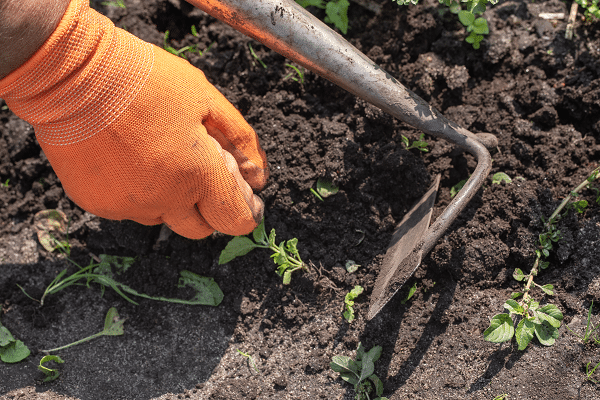
Managing Weeds Organically
Weeds can be a persistent problem in any garden, and in an organic garden, the use of chemical herbicides is off the table. Nonetheless, there are many natural methods for weed control that are both effective and eco-friendly. Mulching, for example, not only suppresses weeds but also helps retain soil moisture and improve soil health. Natural mulch can be made from straw, grass clippings, or even old newspapers.
Manual weeding is another effective method, though it requires a bit more labor. It’s essential to remove weeds before they produce seeds and spread. Tools like a hoe or a hand fork can be useful for this task. However, it’s critical to remember that some level of weeds can be beneficial, as they can attract beneficial insects and increase biodiversity.
Harvesting And Storing Your Produce
The moment of harvest is undoubtedly a highlight for every organic gardener. Knowing when to harvest can make a significant difference in taste and nutritional content. Each vegetable has a prime harvesting time; for example, zucchinis are usually best when they are small and firm, while tomatoes need to be fully colored. It’s crucial to do some research and learn about the best harvesting time for each vegetable planted in the garden.
After harvesting, proper storage is key to maintaining the quality and nutritional content of the produce. Most vegetables can be stored in a cool, dark place, while some need to be refrigerated. Root vegetables like potatoes and onions should be cured before storage to extend their shelf life. Using produce fresh from the garden whenever possible will always provide the most nutritious and delicious results.
Conclusion
In this guide, key practices for a successful organic vegetable garden have been thoroughly discussed. From the importance of soil health and natural pest control to the relevance of climate in choosing vegetables, understanding these factors will significantly improve gardening outcomes. The benefits of such a garden extend beyond fresh produce – it’s a step towards sustainability, providing a chance to contribute positively to the environment while also enriching personal health. May this inspire aspiring gardeners to start their journey into organic gardening, and may seasoned ones discover new strategies to implement in their gardens.